Types of Hearing Loss Information
The symptoms, the causes, the prevention and the facts of hearing loss
| Hearing Aid UK 05/01/2026 Update |
Hearing loss is common
Hearing loss can be categorised into three main types: conductive, sensorineural, and mixed. Conductive hearing loss happens when sound waves are blocked from reaching the inner ear, while sensorineural hearing loss is caused by damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve.
Mixed hearing loss is a combination of both conductive and sensorineural loss. When we generalise hearing loss, it is the partial or total inability to hear sounds in one or both ears.
It is a common condition that can affect people of all ages, from infants to the elderly. While it can be a temporary or permanent condition, hearing loss can have a significant impact on daily life and overall well-being.
On this page, we go through the types, the symptoms, the causes, the preventions and the facts of hearing loss so you are better informed of the condition.

Latest hearing loss statistics in the UK
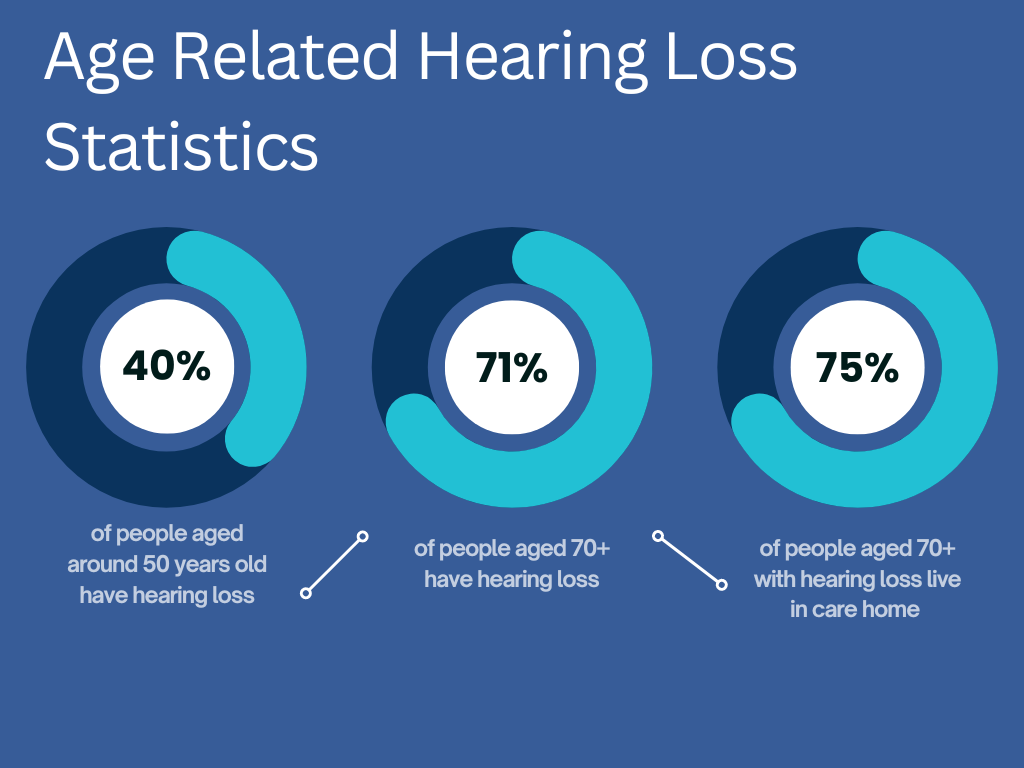
- 1 in 6 of the UK’s adults are affected by hearing loss.
- 11 million people have hearing loss in the UK.
- 6.7 million would benefit from hearing aids; however, only 2 million people wear them.
- Around 900,000 people are severely or profoundly deaf.
- 60-70% of people with hearing loss live in a care home.
- 1/3 of people aged 65+ have hearing loss.
- Hearing loss ranks third for disease burden in the UK.
- It is estimated that by 2035, a fifth of the population will have age-related hearing loss.
All statistics taken from the World Health Organisation (WHO)

The difference between 'normal' hearing and hearing loss
In a different study, MRI scans of people with severe hearing loss were compared with those of people with 'normal hearing'.
These scans showed that the auditory cortex was smaller in those with hearing loss.
This backs up the theory that unused parts of the brain start to shrink or disappear when they are not used.
Once brain cells are lost, they are not replaced. Whilst everyone’s brain begins to shrink as they age, the scans of people with normal hearing had a larger auditory cortex.
This means that there was no change in their ability to recognise and process sounds.
Hearing Loss Definition
Hearing loss levels and specifications
What are the levels of hearing loss?
There are several causes of hearing loss, including prolonged exposure to loud noises, ear infections, ageing, genetics, certain medications, and head injuries.
In some cases, hearing loss may be present from birth, known as congenital hearing loss. Certain medical conditions, like otosclerosis and Meniere's disease, can also contribute to hearing loss.
The true definition of hearing loss is when your ability to hear speech and other sounds is greatly reduced. Hearing loss cannot be cured, but can be successfully treated with hearing aids dispensed by an audiologist.
It is separated into categories and levels of classifications, such as mild hearing loss, moderate hearing loss, severe hearing loss or profound hearing loss.
Putting hearing loss into perspective
If you have mild hearing loss, the quietest sounds you can hear (with your better ear) are anywhere between 25 and 40 dB. If you have moderate hearing loss, the quietest sounds will be between 40 and 70 dB. If you have a severe to profound hearing loss, this range would be between 70 and 95 (or higher) dB.
Humans hear sounds in a frequency range from 20 Hz to 20 kHz; however, the upper limit in average adults is often closer to 15–17 kHz. These hearing loss categories are normally specified using a measured audiometric average of 500, 1000, 2000 and 4000 Hz.
Hearing Loss Information
The main types of hearing loss
There are various severities of hearing loss. Below are hearing loss classifications:
The severity of hearing loss can vary from mild to profound. In mild cases, you may struggle to hear soft sounds or understand speech in noisy environments.
Moderate hearing loss may result in difficulty hearing conversations, while severe and profound hearing loss can lead to a complete inability to hear sounds, including speech.
Mild hearing loss
What is mild hearing loss? When you have mild hearing loss, you are unable to distinguish sounds that are quieter than 25 decibels (dB) for adults and 15 decibels for children.
Sounds such as whispered conversations, water dripping, the rustling of leaves and birds chirping are some examples of sounds you can lose when you have mild hearing loss.
With mild hearing loss, you may also struggle to hear low-pitched and high-pitched frequency sounds. However, most people with mild hearing loss lose the ability to hear high-pitched sounds first.
Although this level of hearing loss sounds rather tame, it still requires urgent medical assistance, as it can lead to other medical problems if untreated.
Related reading: Read more about mild hearing loss
Moderate hearing loss
What is moderate hearing loss? Generally, quiet sounds heard by your better ear are between 35 and 49 dB.
Moderate hearing loss is generally when you have issues hearing in many situations and struggle to keep up and understand speech in conversation. People with moderate hearing loss are usually treated with and benefit from wearing hearing aids.
Related reading: Read more about moderate hearing loss
Moderately severe hearing loss
What is moderately severe hearing loss? Generally, quiet sounds heard by your better ear are between 50 - 64 dB. People who suffer from moderately severe hearing loss have problems hearing in most situations when not using digital hearing aids.
Related reading: Read more about moderate to severe hearing loss
Severe hearing loss
What is severe hearing loss? Generally, quiet sounds heard from your better ear are between 65 - 79 dB. Those with severe hearing loss are classed as very hard of hearing and struggle to hear all frequencies.
Severe hearing loss requires you to wear powerful hearing aids or implants. They might also rely on lip-reading and sign language, as well as wearing hearing aids.
Related reading: Read more about severe hearing loss
Profound hearing loss
What is profound hearing loss? Generally, quiet sounds are heard between 80 dB and above in your better ear. Those with profound hearing loss have extremely weak hearing and require very powerful hearing aids or cochlear implants. They also rely on lip-reading and sign language.
Related reading: Read more about profound hearing loss

Hearing Loss Types
The main effects of hearing loss
Hearing loss can have a wide range of consequences
The consequences of hearing loss vary with each individual. It can affect an individual's ability to communicate effectively, leading to difficulties in personal relationships and professional settings.
It can also impact a person's quality of life, as they may miss out on important conversations, social gatherings and enjoyable activities. Fortunately, there are various treatment options available for hearing loss.
However, most people with a hearing impairment can suffer from anxiety, depression, and social, psychological and physical problems due to their hearing loss. Audiologists, ENT clinics, hearing coaches and hearing organisations are brilliant sources of research, support, advice, treatment and rehabilitation.
We will discuss the reason why early diagnosis of hearing loss is essential further down this page, but if you take a proactive approach to your hearing concerns, you will improve the chances of a successful solution.
Hearing loss provides a barrier to communication, which is very much needed to feel connected to the world and is essential to the state of our mental health.
The most common form of treatment is hearing aids, which not only help you to hear better, but also to better understand your soundscape and greatly reduce the risks of developing dementia.
What are the different types of hearing loss?
Hearing loss is classified as sensorineural hearing loss, conductive hearing loss or mixed hearing loss. Here we break down each type of hearing loss:
Sensorineural hearing loss
This type of hearing loss is due to the tiny hair cells in the inner ear being damaged. Sensorineural hearing loss can be linked to age-related hearing loss (also known as Presbycusis) and noise-induced hearing loss, caused by long periods of exposure to loud noise.
Related reading: Read more about sensorineural hearing loss
Conductive hearing loss
Conductive hearing loss is a type of hearing loss when the ears’ ability to conduct sound from the outer ear through the middle ear into the inner ear is blocked or reduced.
Related reading: Read more about conductive hearing loss
Mixed hearing loss
If there are issues with conducting sound and there is damage to the inner ear hair cells, it is called mixed hearing loss; therefore, this type of hearing loss is a combination of sensorineural hearing loss and conductive hearing loss.
Related reading: Read more about mixed hearing loss
Auditory processing hearing loss
This is an auditory processing disorder (APD) and a form of hearing loss, unlike the other three main kinds. It is when there is no other form of hearing loss present, the ears are fully capable of receiving sound, but the brain has problems processing and understanding it.
Related reading: Read more about Auditory Processing Disorder

Hearing Loss Information
Other types of hearing loss
Bilateral hearing loss: Bilateral hearing loss is in both ears, which sometimes is caused by children with Pendred syndrome - a genetic disease that causes this type of hearing loss.
Unilateral hearing loss: Unilateral hearing loss, also known as single-sided deafness (SSD) or hearing loss in one ear, is a hearing loss in one ear. Treatment is usually a CROS hearing aid system.
Asymmetric hearing loss: Asymmetric hearing loss (AHL) is when the hearing loss you have in both ears is significantly different.
Hidden hearing loss: Hidden hearing loss is defined as a hearing loss that's not detectable on standard hearing tests/ audiograms, which highlight issues within the ear.
High-frequency hearing loss: High-frequency hearing loss is when high-pitched sounds are harder to hear. It can affect anyone of any age, but it is more commonplace in older adults with age-related hearing loss and those who are exposed to loud noises.
Here are some symptoms of hearing loss and signs of hearing loss to look out for:
- Difficulty understanding words, especially in noisy environments.
- Muffled speech and sound.
- Trouble hearing consonants.
- Frequently asking people to repeat themselves or to speak more slowly and loudly.
- Constantly having to turn up the volume on audio.
- Withdrawal from conversations.
- Avoiding social gatherings.
Why is early treatment and diagnosis for hearing loss essential?
If you delay getting a hearing aid, you could be causing more damage to your future hearing health. Over time, without amplification, your perception of sound can change. This is because when you hear a sound, your ears detect a vibration in the air and transmit it via the inner ear to the auditory nerve.
This nerve carries signals to the brain, which then processes them into the noise and speech sounds that create the soundscape around you.
In order for the auditory cortex to function, it needs to be used. Just like any other muscle in the body. If you have hearing loss that is untreated your brain starts to get weak. If you stop using a part of it or signals can no longer reach it, it will send it elsewhere.
Studies show that people who have untreated hearing loss and the hearing nerve and auditory cortex haven't been used - were unable to processing the sound in recognisable words.
People with normal hearing have an active brain that can pick out speech sounds from challenging background noise, distinguish them and understand them. Therefore, early diagnosis of hearing loss is vital.

Types of Hearing Loss
The stigmas surrounding hearing loss
Why don’t people get hearing aids straight away?
Perhaps they feel there’s a stigma around wearing hearing aids. They don’t want to be seen as getting old. In reality, they don’t realise just how small and discrete modern hearing aids are. But the longer you ignore any hearing problems, the worse your hearing will get.
Hearing aids can keep the hearing nerves and brain stimulated and healthy. This means that even if your hearing does begin to get worse over time, with the right amplification, you will still be able to process sounds and conversation.
Remember, your hearing aids may not be perfect right away. If you’ve had untreated hearing loss for some time, it could take a while for your brain to get used to noise again.
Related reading: Getting used to new hearing aids
A fast hearing loss diagnosis is key
The sooner you get help and advice about your hearing loss and get hearing aids, the easier it will be to get used to them. Early intervention will also prevent further hearing difficulties by ensuring that the hearing nerves and auditory cortex are used to their full potential.
Hearing loss community and support
There are now more online hearing loss communities and forums where you can ask questions, share ideas and connect with others who have hearing loss. There are also hearing loss organisations and charities that can support you and organise events to bring people together.
Organisations such as Action on Hearing Loss (now called RNID - The Royal National Institute for Deaf) are a great example of this.
Getting your hearing checked regularly is important for a multitude of reasons
Firstly, it helps in detecting any potential hearing problems at an early stage, allowing for timely intervention and treatment. Early detection can prevent further damage to your hearing and improve your overall quality of life.
Secondly, a hearing test can identify the specific type and degree of hearing loss, enabling audiologists to recommend personalised solutions such as hearing aids that are tailored to your needs.
This can greatly enhance your ability to communicate and engage in various activities. Additionally, regular hearing check-ups can help monitor changes in hearing health, ensuring timely adjustments and maintenance of hearing devices.
What causes hearing loss?
But first, how do we hear?
To fully understand hearing loss, it's useful to understand how you hear and what decibels are safe. Our ears are made up of three major areas - the outer ear, middle ear and inner ear.
Sound waves go through the outer ear and cause vibrations at the eardrum, which in turn amplify these vibrations down to the inner ear.
The vibrations go through fluid in a snail-shaped structure of the inner ear - the cochlea.
Attached to the nerve cells in the inner ear, there are thousands of small hairs that assist in translating sound vibrations into electrical signals, which are then sent to the brain.
This is when your brain switches them into sound.
Hearing loss causes and a ruptured eardrum
A ruptured eardrum, also known as a Tympanic Membrane Perforation, is when loud spurts of sound, sudden changes in air pressure or an infection can cause your eardrum to rupture.

Hearing loss caused by loud noises
If you expose your ears to loud noises for a prolonged period of time it can damage the cells in your inner ear.
This long-term damage can also be caused by short, sudden or sharp bursts of noise and is called noise-induced hearing loss.
Understanding sound decibels in common noises
It is also important to understand what sound levels are safe and what levels are considered to be risking permanent future damage to your hearing, if exposed to them for a long duration of time.
Therefore, the louder the noise, the less time it takes to cause permanent hearing damage. In general terms, anything over 75dB is considered high risk.
Here are a few examples: Whisper - 60 dB, fridge - 40 dB, general conversation - 60 dB, dishwasher - 70 dB, car commuter traffic - 85 dB, motorbike - 95 dB and live gigs - 110 dB.
The Causes of Hearing Loss
What are the common causes?
Hearing loss caused by ear infections / fungal ear infection
There are many common causes of hearing loss. You can get hearing loss after an ear infection, ear fungus or abnormal bone growth or tumours in the outer or middle ear. Any of these can cause hearing loss. This type of hearing loss is usually temporary and decreases in severity after diagnosis and treatment.
Your doctor might treat your ear infection with a course of antibiotics, which should eventually assist in getting your hearing back to normal. Sometimes people are prone to getting ear infections, and in this case, doctors might insert a tube in your eardrum and drain out any fluid.
Hearing loss due to age, hearing loss in the elderly and hearing loss caused by damage to the inner ear
When we age, the tiny hairs and nerve cells in the cochlea of the inner ear are affected. This deflects the sound signals to the brain. If these hairs or nerve cells are damaged or missing, the electrical impulses can't be transmitted properly, causing hearing loss.
This results in the inability to hear higher-pitched tones, and these sounds may become muffled. You will also find a conversation in noise very difficult to understand. This type of hearing loss is called Presbycusis.
Related reading: Age-related hearing loss
Hearing loss causes and genetics
Genetic hearing loss is when your genetic makeup may dictate that you are more at risk of getting ear damage or sound deterioration over time due to heredity issues. Genetic factors cause some people to be more susceptible to hearing loss than others.
This is because their genes make them more vulnerable to hearing loss - either through age, noise, medication or infections. Studies have shown that around 35-55% of hearing loss is caused by age and genetics combined.
Everyone has genes existing in two copies passed down from their mother and father. The risk of hearing loss usually depends on whether a mutation is dominant or recessive.
A dominant mutation causes hearing loss if only one of the inherited copies from the parent is damaged. A recessive mutation only causes hearing loss if both copies are damaged.
Related reading: Hereditary hearing loss
Hearing loss caused by earwax
A gradual buildup of earwax can cause hearing loss. If not treated and removed, it blocks the ear canal and prevents the conduction of sound waves. Earwax removal or micro-suction can help restore your hearing safely and painlessly.
While earwax is important for hearing health, a common problem is too much earwax in the ear canal. In the UK, it is estimated that 2.3 million people have issues with excessive earwax each year.
Hearing loss caused by medication and illness
There are a few types of medications that can potentially damage the inner ear or cause tinnitus and temporary hearing loss. There are also some illnesses or diseases that result in a high fever and can do harm to the cochlea. This cause of hearing loss is called Ototoxicity.
Related reading: Ototoxicity and hearing loss

Hearing loss treatment with hearing aids
Can hearing loss be cured?
Some hearing loss is temporary; however, most forms of hearing loss are permanent and need an early diagnosis for treatment to be successful and to help you hear better again.
Sensorineural is a type of hearing loss that is permanent. The hair cells that are damaged can't be repaired.
People suffering from this type of hearing loss are generally advised to wear hearing aids by an audiologist.
In some circumstances, cochlear implants are recommended instead. Either way, your audiologist will discuss what treatment to take based on your specific hearing loss needs.

Can hearing aids treat all types of hearing loss?
Hearing aids can effectively treat many types of hearing loss, particularly sensorineural hearing loss and some cases of mixed hearing loss.
Some devices are specifically designed with features to treat specific and related issues, such as hearing aids for Tinnitus relief.
They are not typically used to treat conductive hearing loss, as this type of hearing loss often results from physical blockages or abnormalities in the ear that prevent sound from reaching the inner ear.
In such cases, conductive hearing loss may be treated through medical or surgical interventions, depending on the underlying cause.
Conductive hearing loss treatment
Conductive hearing loss is generally caused by a condition in the outer or middle ear - this is usually temporary.
It is quite common that a build-up of earwax is the culprit, as well as fluid in the middle ear, a perforated eardrum or a 'wet ear'.
This form of hearing loss is commonly treated medically at your ENT clinic.
However, if all efforts to sort the problem are exhausted - or the hearing loss is a mix of both sensorineural and conductive - then other options like hearing aids are usually advised.
The most common solution is hearing aids
These amplify sounds and improve the ability to hear. In some cases, surgery may be recommended to address specific causes of hearing loss.
Such as removing obstructions or repairing damaged structures in the ear. However, prevention is key to maintaining healthy hearing.

What type of hearing loss do cochlear implants help?
Cochlear implants are primarily used to treat severe to profound sensorineural hearing loss.
These devices can be very effective in restoring a sense of hearing for individuals who do not benefit from traditional hearing aids.
It's important to note that cochlear implants are not suitable for all types of hearing loss.
How to treat your hearing loss is made on a case-by-case basis following a thorough evaluation by our audiologists to best suit your type of hearing loss, your needs and lifestyle.

Hearing Loss Information
Can an audiogram show different types of hearing loss?
Hearing test diagnosis
Yes, an audiogram can show different types of hearing loss. An audiogram is a graph that depicts a person's hearing sensitivity across a range of frequencies.
The two primary types of hearing loss that can be identified on an audiogram are sensorineural hearing loss and conductive hearing loss. In some cases, mixed hearing loss may also be evident.
Additionally, audiograms can provide information about the degree of hearing loss (ranging from mild to profound) and the specific frequencies where hearing is affected. This information is valuable in diagnosing the type and degree of hearing loss, as well as determining appropriate treatment options.
It's important to note that an audiogram is just one part of the diagnostic process for hearing loss, and a comprehensive evaluation by an audiologist or otolaryngologist is necessary to determine the cause and appropriate treatment for the individual's specific hearing loss.
Testing can greatly enhance your ability to communicate and engage in various activities. Additionally, regular hearing check-ups can help monitor changes in hearing health, ensuring timely adjustments and maintenance of hearing devices.
Summary
Avoiding exposure to loud noises, wearing ear protection in noisy environments and taking precautions to prevent ear infections can help reduce the risk of hearing loss. Hearing loss is a common condition that can have a significant impact on life.
Understanding the causes and available treatment options is essential in managing and mitigating the effects of hearing loss.
Hearing aids and hearing loss treatment near me
It helps in detecting any potential hearing problems at an early stage, allowing for timely intervention and treatment. Early detection can prevent further damage to your hearing and improve your overall quality of life.
A hearing test can identify the specific type and degree of hearing loss, enabling audiologists to recommend personalised solutions such as hearing aids that are tailored to your needs.
If you think you have hearing loss or know someone who might - book a free hearing healthcare consultation with one of our audiologists local to you today.
Call us free on 0800 567 7621
Hearing loss awareness articles you might like...
 How to tell if hearing loss is permanent or temporary
How to tell if hearing loss is permanent or temporary  What is Mastoiditis?
What is Mastoiditis?  What is Vestibular Neuritis?
What is Vestibular Neuritis? Our specialist service includes:
Do not spend hundreds of pounds without getting a second opinion from us.
Please call us on 0800 567 7621
 Not only are the prices great, but the service is fantastic! Many thanks to your team.
Not only are the prices great, but the service is fantastic! Many thanks to your team.Why choose Hearing Aid UK to help you find the best hearing aids for you?
What's included in our hearing aid prices?
Other pages you might find useful
Common FAQs when researching hearing loss and hearing aids
In general, any audiologist will always recommend to you the hearing aid model that best suits your needs. Here is a useful checklist to make sure that is the case.
- Audiologist's level of knowledge: The audiologist you have seen will hopefully have a wide knowledge of all available hearing aids; however, some will only be familiar with a small number of brands and, therefore, may not really be in a position to know which model is the best for you. It is OK to challenge their recommendation and ask them to justify why this particular brand is the one for you.
- Do research: Read about the hearing aid that was recommended. Does it seem like it will suit your lifestyle? Does it have more or fewer features than you need?
- Be aware of sales targets: Many high street retailers have specific tie-ins to a particular manufacturer/brand. The hearing aid they have suggested may still be the correct one for you, but do your research so that you know why they might have recommended it.
If you have significant hearing loss in both ears, you should be wearing two hearing aids. Here are the audiological reasons why:
Localisation: The brain decodes information from both ears and compares and contrasts them. By analysing the minuscule time delays as well as the difference in the loudness of each sound reaching the ears, the person is able to accurately locate a sound source.
Simply put, if you have better hearing on one side than the other, you can't accurately tell what direction sounds are coming from.
Less amplification is required: A phenomenon known as “binaural summation” means that the hearing aids can be set at a lower and more natural volume setting than if you wore only one hearing aid.
Head shadow effect: High frequencies, the part of your hearing that gives clarity and meaning to speech sounds, cannot bend around your head. Only low frequencies can. Therefore, if someone is talking on your unaided side, you are likely to hear that they are speaking, but be unable to tell what they have said.
Noise reduction: The brain has its own built-in noise reduction, which is only really effective when it is receiving information from both ears. If only one ear is aided, even with the best hearing aid in the world, it will be difficult for you to hear in background noise as your brain is trying to retain all of the sounds (including background noise) rather than filtering them out.
Sound quality: We are designed to hear in stereo. Only hearing from one side sounds a lot less natural to us.
Fancy some further reading on this topic? You can read about why two hearing aids are better than one in our article, hearing aids for Both Ears, here
For most people, the main benefit of a rechargeable hearing aid is simple convenience. We are used to plugging in our phones and other devices overnight for them to charge up. Here are some other pros and cons:
For anybody with poor dexterity or issues with their fingers, having a rechargeable aid makes a huge difference, as normal hearing aid batteries are quite small and some people find them fiddly to change.
One downside is that if you forget to charge your hearing aid, then it is a problem that can't be instantly fixed. For most, a 30-minute charge will get you at least two or three hours of hearing, but if you are the type of person who is likely to forget to plug them in regularly, then you're probably better off with standard batteries.
Rechargeable aids are also a little bit bigger and are only available in Behind-the-Ear models.
Finally, just like with a mobile phone, the amount of charge you get on day one is not going to be the same as you get a few years down the line. Be sure to ask what the policy is with the manufacturer's warranty when it comes to replacing the battery.
For most people, the answer is yes. But it's never that simple.
The majority of hearing problems affect the high frequencies a lot more than the low ones. Therefore, open fitting hearing aids sound a lot more natural and ones that block your ears up can make your own voice sound like you are talking with your head in a bucket. Therefore, in-ear aids tend to be less natural.
However, the true answer is we can't tell until we have had a look in your ears to assess the size of your ear canal, and until we have tested your hearing to see which frequencies are being affected.
People with wider ear canals tend to have more flexibility, also there are open fitting modular CIC hearing aids now that do not block your ears.
There is also the age-old rule to consider, that a hearing aid will not help you if it's sat in the drawer gathering dust. If the only hearing aid you would be happy wearing is one that people can't see, then that's what you should get.
Most people can adapt to any type of hearing aid, as long as they know what to expect. Have an honest conversation with your audiologist as to what your needs are.
Generally speaking, six or more. Unless it's none at all. The number of channels a hearing aid has is often a simplistic way an audiologist will use to explain why one hearing aid is better than another, but channels are complex, and it is really not that straightforward. Here are some reasons why:
Hearing aids amplify sounds of different frequencies by different amounts. Most people have lost more high frequencies than low, and therefore need more amplification in the high frequencies. The range of sounds you hear is split into frequency bands or channels, and the hearing aids are set to provide the right amount of hearing at each frequency level.
Less than six channels, and this cannot be done with much accuracy, so six is the magic number. However, a six-channel aid is typically very basic with few other features and is suitable only for hearing a single speaker in a quiet room. The number of channels is not what you should be looking at; it's more the rest of the technology that comes with them.
As a final note, different manufacturers have different approaches. One method is not necessarily better than any other. For example, some manufacturers have as many as 64 channels in their top aids. Most tend to have between 17 and 20. One manufacturer has no channels at all.
Manufacturer's warranties typically last between 2-5 years, depending on the brand and model, and cover defects in materials and workmanship. This includes repairs for component failures, electronic malfunctions, and manufacturing defects, but excludes damage from misuse, accidents, or normal wear. Most manufacturers also include loss and damage insurance for the first year.
We handle all warranty claims on your behalf, liaising with manufacturers and ensuring you get replacement devices quickly when needed. This comprehensive warranty coverage, combined with our lifetime aftercare, gives you complete peace of mind.
Our hearing tests are completely free, whether at our clinics or in your home. Unlike other providers who charge £30-£100 for home visits, we believe hearing healthcare should be accessible without financial barriers. Our comprehensive assessments include examination by a registered audiologist, audiogram results, and personalised recommendations.
All testing, future adjustments, and ongoing support are included at no extra cost. While NHS tests are also free, typical 6-week waiting periods often lead people to seek immediate private testing. We provide prompt, professional assessments that fit your schedule and budget.
Yes, we offer completely free home visits throughout the UK, and this service is included in our prices with no additional charges. Home visits are particularly valuable for people with mobility issues, busy schedules, or those who simply prefer the comfort and convenience of their own environment.
Our audiologists can conduct full hearing tests, fit hearing aids, and provide ongoing support in your home. This service sets us apart from many providers who either don't offer home visits or charge extra for them.
We can offer prices up to 40% lower than high street retailers because of our business model. As a network of 200+ independent audiologists, we don't have the massive overheads of large retail chains - no expensive high street premises, no sales targets pushing audiologists to sell the most expensive options, and no costly marketing campaigns.
However, we maintain the same buying power as the big chains because we purchase on behalf of our entire nationwide network. This means you get access to the same premium hearing aids with professional service, but at genuinely competitive prices.
We offer a comprehensive 60-day money-back guarantee, which gives you twice the industry standard time to properly assess whether your hearing aids are right for you. This extended period recognises that adjusting to hearing aids takes time, and your brain needs several weeks to adapt to the amplified sounds.
Unlike many providers who offer just 30 days, we believe 60 days gives you the confidence to test your hearing aids in all the situations that matter to you - from quiet conversations at home to busy restaurants and outdoor activities.
Ask the Experts
6 Morton Lane
Walkwood
Redditch
Worcestershire
B97 5QA
Latest Launch
When we refer to a product as 'Latest Launch', we mean it is the latest to be released on the market.
New
When we refer to a product as 'New', we mean that the product is the newest hearing aid model on the market.
When we refer to a product as 'Superseded', we mean that there is a newer range available which replaces and improves on this product.
Older Model
When we refer to a product as an 'Older Model', we mean that it is has been superseded by at least two more recent hearing aid ranges.

