
Head of Online Medical Content

Audiology Expert

What is Moderate Hearing Loss?
Understanding moderate hearing loss
Overview | What is moderate hearing loss? | Different hearing loss levels | What it feels like to have moderate hearing loss | What to do about it | Key takeaways | Summary
Last Hearing Aid UK Update: 20
Overview
Moderate hearing loss is a middle level of hearing difficulty where everyday sounds and conversations seem quieter and harder to understand. It can cause fatigue, stress, and social withdrawal because the brain must work harder to process sound.
Challenges are especially noticeable in noisy environments, such as social gatherings or phone calls.
Fortunately, modern hearing aids can effectively improve hearing and quality of life. If you recognise these signs, getting a professional hearing test by a hearing aid provider, like Hearing Aid UK, is an important next step.
Not a little, not a lot
We often talk about hearing loss in extremes, such as profound and severe, or just a bit 'hard of hearing'. But what about that middle ground?
Such as when you're not completely cut off from the world of sound, but things definitely aren't as clear as they used to be, that's where moderate hearing loss comes in.
Even though it's not too little, not too much, it is definitely enough to cause a fair bit of disruption to your daily life. So, let's have a look at what moderate hearing loss actually is, how it might be affecting you, and what can be done about it.
What is moderate hearing loss?
Hearing loss is measured in decibels (dB), and normal hearing means you can hear relatively quiet sounds, like a whisper or the rustling of leaves. Moderate hearing loss, on the other hand, means you can only hear sounds that are a bit louder.
With moderate hearing loss, those everyday sounds, like the TV at a reasonable level, a chat with a friend in the cafe, or the doorbell ringing, all need to be louder for you to hear and understand them.
What causes moderate hearing loss?
Understanding the underlying causes of moderate hearing loss early can help with future prevention and treatment. Common causes include:
- Age-related hearing loss (presbycusis): The most common cause, typically developing gradually over time as the delicate hair cells in the inner ear naturally deteriorate as we age.
- Noise exposure: Prolonged exposure to loud noises can damage the inner ear, leading to moderate hearing loss over time.
- Ear infections: Chronic or severe ear infections, particularly in childhood, can result in permanent hearing damage if left untreated.
- Ototoxic medications: Certain medicines, including some antibiotics, chemotherapy drugs, and high doses of aspirin, are known to damage hearing.
- Genetics: Some people inherit a predisposition to hearing loss, which may manifest as moderate hearing loss in adulthood.
- Medical conditions: Diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and autoimmune disorders can affect blood flow to the inner ear, potentially causing hearing loss.
- Head trauma: Injuries to the head or ear can damage the structures responsible for hearing.
Here is an overview of the different levels of hearing loss and what you would generally struggle with in that range:
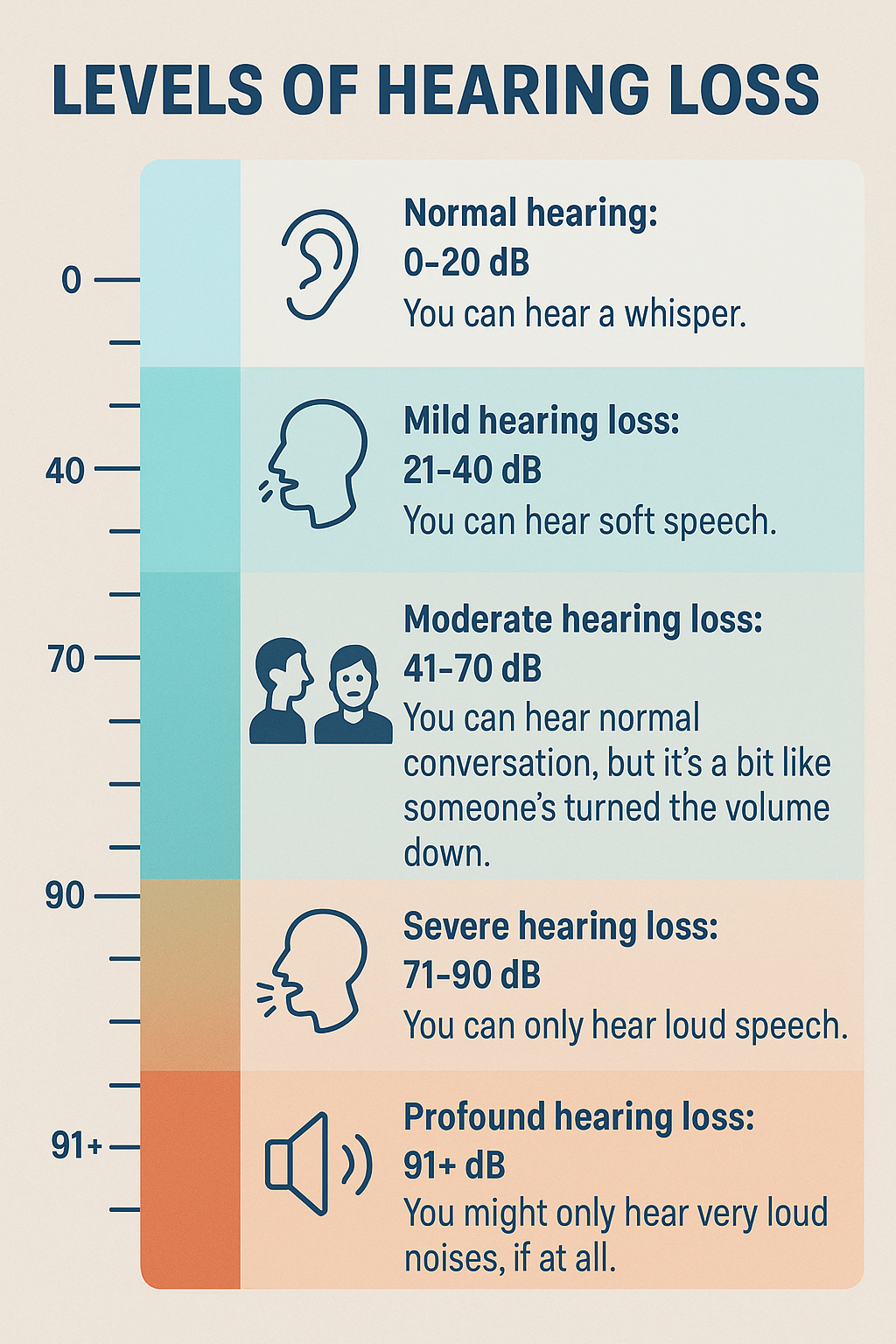
- Normal hearing: 0-20 dB - You can hear a whisper.
- Mild hearing loss: 21-40 dB - You can hear soft speech.
- Moderate hearing loss: 41-70 dB - You can hear normal conversation, but it's a bit like someone's turned the volume down.
- Severe hearing loss: 71-90 dB - You can only hear loud speech.
- Profound hearing loss: 91+ dB - You might only hear very loud noises, if at all.
It's important to understand that moderate hearing loss isn't just about missing the odd word here and there, but about the effort it takes to actually hear.
When you have normal hearing, listening is something you do without even thinking about it. But when you have moderate hearing loss, your brain has to work much harder to process sound and understand it.
This can lead to:
- Fatigue: You might feel tired and drained after social events or situations where you've had to concentrate hard on listening.
- Stress: The constant struggle to hear can make you feel stressed, anxious, or even a bit irritable.
- Social withdrawal: You might start avoiding social situations because you're worried about not being able to hear, which can lead to feelings of isolation.
- Difficulty concentrating: You might find it harder to focus on tasks, as your brain is too busy trying to process sound.
Related reading: Digital and listening fatigue
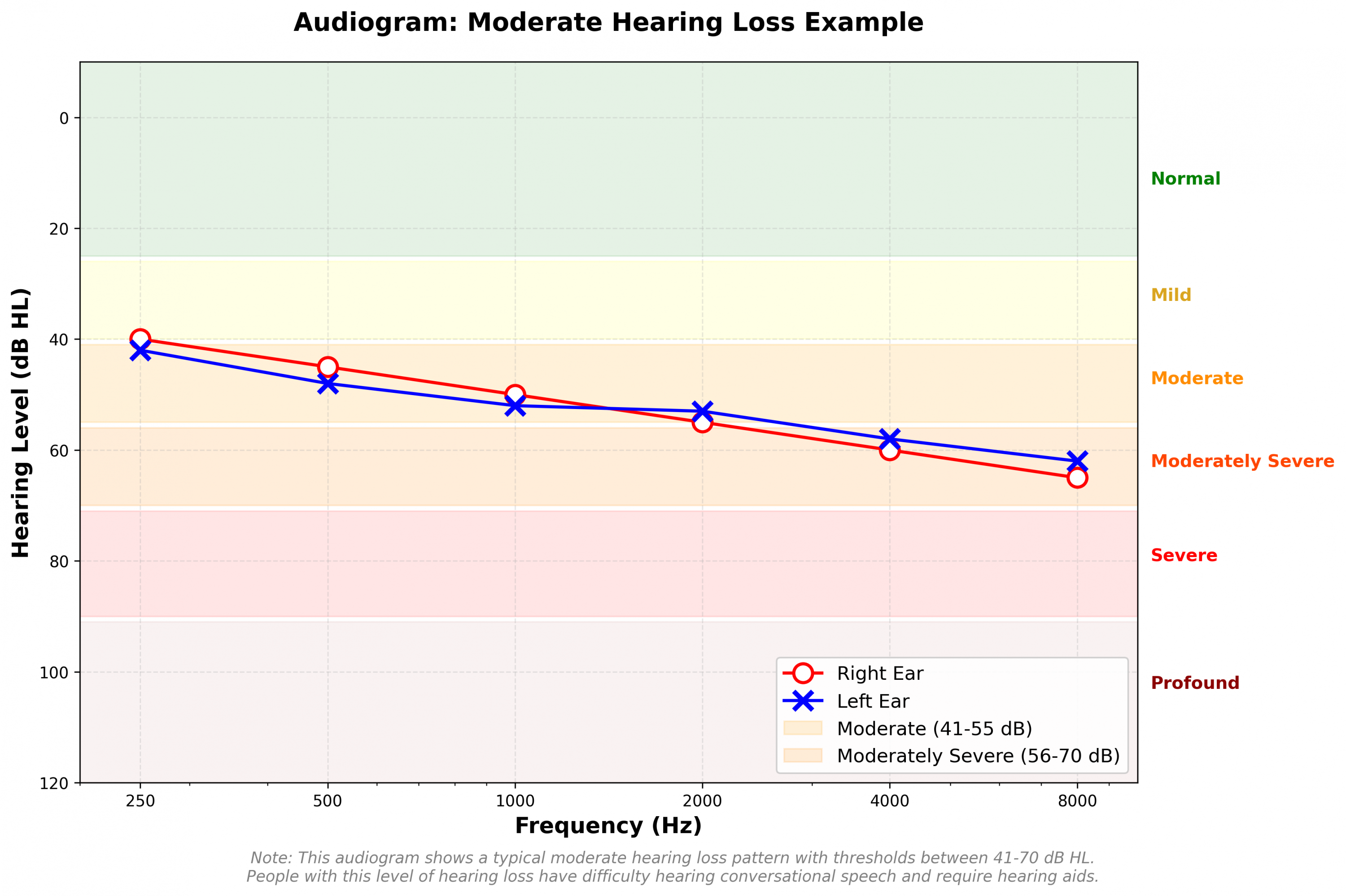
Moderate hearing loss in one ear vs both ears
Moderate hearing loss can affect one ear (unilateral) or both ears (bilateral). Each comes with its own unique challenges, such as:
- Unilateral moderate hearing loss: When only one ear is affected, you may struggle with sound localisation (determining where sounds are coming from) and hearing speech in noisy environments. You might find yourself turning your "good ear" towards speakers.
- Bilateral moderate hearing loss: When both ears are affected, communication difficulties are generally more pronounced, especially in group settings and noisy environments. However, hearing aids for both ears can provide better overall sound quality and spatial awareness.
Your audiologist will assess whether you have unilateral or bilateral hearing loss during your hearing assessment and recommend the most suitable hearing solution.
What it feels like to have moderate hearing loss
In quiet environments, you might hear and get by, you can have a one-on-one conversation without too much trouble, and you can also enjoy your favourite radio show without cranking up the volume.
However, when things get a bit noisier, such as more background noise, that's when the challenges really start to be felt.
Here are some real-life experiences you might recognise:
- The pub quiz: You're out with your friends, and between the quizmaster's voice, the chatter of the other teams, and the clinking of glasses, you're struggling to keep up.
- Family gatherings: It's your birthday party, and everyone's gathered at your house. The kids are running around, your friend is trying to tell you a story, and there's music playing in the background.
Eventually, you find yourself constantly asking people to repeat themselves, and you are left feeling exhausted.
- The theatre: You're having a hard time following the dialogue, especially during the quieter moments.
- Phone calls: On the phone, you keep saying "Pardon?" and "Could you speak up a bit?", which can be awkward for both people involved.
Related reading: I'm finding it difficult to hear on the phone
What's the next step?
Moderate hearing loss cannot be cured; however, the good news is that moderate hearing loss can often be effectively managed. The most common solution is hearing aids, and modern hearing aids are more technologically and aesthetically pleasing than those of the past.
They're small, discreet, and packed with clever technology that can make a real difference to your hearing.
In short, a hearing aid works by amplifying the sounds around you, making them louder and clearer. An audiologist will be able to assess your hearing and recommend the best type of hearing aid for your needs.
If you recognise any of the situations or symptoms described above, it's definitely worth getting your hearing checked. You can start by contacting your local audiologist for a hearing assessment.
A hearing test is quick, painless, and can provide you with valuable information about your hearing health. And if it turns out you do have moderate hearing loss, remember that there are solutions available that can help you enjoy a better quality of life.
Contact us today to schedule a free hearing assessment, either in a local clinic or at your home with one of our professional audiologists.
Key takeaways
- Moderate hearing loss sits in the 41-70 dB range: You can hear normal conversation, but it sounds as though someone's turned the volume down on everyday life.
- It's the "middle ground" that's easy to overlook: Not severe enough to feel urgent, but disruptive enough to significantly impact your daily activities and relationships.
- Your brain works overtime to compensate: The constant effort to process and understand sound leads to listening fatigue, stress, and exhaustion after social events.
- Quiet environments are manageable, noisy ones are challenging: One-to-one conversations at home might be fine, but pubs, restaurants, family gatherings, and phone calls become increasingly difficult.
- Social withdrawal is a common consequence: Many people with moderate hearing loss begin avoiding situations where they struggle to hear, leading to isolation and reduced quality of life.
- Modern hearing aids are highly effective at this level: Today's devices are small, discreet, and packed with technology specifically designed to amplify speech and reduce background noise.
- Early intervention makes a difference: The sooner you address moderate hearing loss with hearing aids, the easier it is for your brain to adapt and the better your long-term outcomes.
- A hearing test is the first step: Quick, painless, and available free through the NHS or privately. A professional assessment will determine the extent of your hearing loss and the best treatment options.
Summary
Moderate hearing loss, measured between 41-70 decibels, means normal sounds, like conversations or the TV, need to be louder to be heard clearly.
It’s more than just missing words; it requires extra mental effort to listen, often leading to fatigue, stress, and social withdrawal.
While quiet settings may feel manageable, noisy environments can make hearing especially challenging. Real-life scenarios include struggling at family gatherings, phone calls, or in public places. Modern, discreet hearing aids can amplify sounds and improve understanding.
If you experience these symptoms, a hearing assessment from an audiologist can diagnose the issue and offer solutions to enhance your hearing and daily life.
Why Choose Us?
- FREE Hearing Tests
- Best Hearing Aids and Prices
- FREE Aftercare for Life
- FREE Home Visits
- 200+ Local Audiologists
- 60 Day Money Back Guarantee
Think you might have moderate hearing loss?
Moderate hearing loss is a middle ground between normal hearing and severe hearing loss, where everyday sounds need to be louder to be heard.
It can make social situations, like pub quizzes, family gatherings, and phone calls, challenging.
This type of hearing loss isn't just about missing words; it's about the effort it takes to hear, leading to fatigue, stress, and social withdrawal.
Fortunately, it can often be managed effectively with hearing aids, and early detection is key.
Other hearing loss awareness articles you might like...
 Hearing aid stigma
Hearing aid stigma  How to tell if hearing loss is permanent or temporary
How to tell if hearing loss is permanent or temporary  Ways to keep your ears healthy
Ways to keep your ears healthy Our specialist service includes:
Do not spend hundreds of pounds without getting a second opinion from us.
Please call us on 0800 567 7621
 Not only are the prices great, but the service is fantastic! Many thanks to your team.
Not only are the prices great, but the service is fantastic! Many thanks to your team.What's included in our hearing aid prices?
Watch the NHS hearing loss video below
Other pages you might find useful
FAQs
In general, any audiologist will always recommend to you the hearing aid model that best suits your needs. Here is a useful checklist to make sure that is the case.
- Audiologist's level of knowledge: The audiologist you have seen will hopefully have a wide knowledge of all available hearing aids; however, some will only be familiar with a small number of brands and, therefore, may not really be in a position to know which model is the best for you. It is OK to challenge their recommendation and ask them to justify why this particular brand is the one for you.
- Do research: Read about the hearing aid that was recommended. Does it seem like it will suit your lifestyle? Does it have more or fewer features than you need?
- Be aware of sales targets: Many high street retailers have specific tie-ins to a particular manufacturer/brand. The hearing aid they have suggested may still be the correct one for you, but do your research so that you know why they might have recommended it.
If you have significant hearing loss in both ears, you should be wearing two hearing aids. Here are the audiological reasons why:
Localisation: The brain decodes information from both ears and compares and contrasts them. By analysing the minuscule time delays as well as the difference in the loudness of each sound reaching the ears, the person is able to accurately locate a sound source.
Simply put, if you have better hearing on one side than the other, you can't accurately tell what direction sounds are coming from.
Less amplification is required: A phenomenon known as “binaural summation” means that the hearing aids can be set at a lower and more natural volume setting than if you wore only one hearing aid.
Head shadow effect: High frequencies, the part of your hearing that gives clarity and meaning to speech sounds, cannot bend around your head. Only low frequencies can. Therefore, if someone is talking on your unaided side, you are likely to hear that they are speaking, but be unable to tell what they have said.
Noise reduction: The brain has its own built-in noise reduction, which is only really effective when it is receiving information from both ears. If only one ear is aided, even with the best hearing aid in the world, it will be difficult for you to hear in background noise as your brain is trying to retain all of the sounds (including background noise) rather than filtering them out.
Sound quality: We are designed to hear in stereo. Only hearing from one side sounds a lot less natural to us.
Fancy some further reading on this topic? You can read about why two hearing aids are better than one in our article, hearing aids for Both Ears, here
For most people, the main benefit of a rechargeable hearing aid is simple convenience. We are used to plugging in our phones and other devices overnight for them to charge up. Here are some other pros and cons:
For anybody with poor dexterity or issues with their fingers, having a rechargeable aid makes a huge difference, as normal hearing aid batteries are quite small and some people find them fiddly to change.
One downside is that if you forget to charge your hearing aid, then it is a problem that can't be instantly fixed. For most, a 30-minute charge will get you at least two or three hours of hearing, but if you are the type of person who is likely to forget to plug them in regularly, then you're probably better off with standard batteries.
Rechargeable aids are also a little bit bigger and are only available in Behind-the-Ear models.
Finally, just like with a mobile phone, the amount of charge you get on day one is not going to be the same as you get a few years down the line. Be sure to ask what the policy is with the manufacturer's warranty when it comes to replacing the battery.
For most people, the answer is yes. But it's never that simple.
The majority of hearing problems affect the high frequencies a lot more than the low ones. Therefore, open fitting hearing aids sound a lot more natural and ones that block your ears up can make your own voice sound like you are talking with your head in a bucket. Therefore, in-ear aids tend to be less natural.
However, the true answer is we can't tell until we have had a look in your ears to assess the size of your ear canal, and until we have tested your hearing to see which frequencies are being affected.
People with wider ear canals tend to have more flexibility, also there are open fitting modular CIC hearing aids now that do not block your ears.
There is also the age-old rule to consider, that a hearing aid will not help you if it's sat in the drawer gathering dust. If the only hearing aid you would be happy wearing is one that people can't see, then that's what you should get.
Most people can adapt to any type of hearing aid, as long as they know what to expect. Have an honest conversation with your audiologist as to what your needs are.
Generally speaking, six or more. Unless it's none at all. The number of channels a hearing aid has is often a simplistic way an audiologist will use to explain why one hearing aid is better than another, but channels are complex, and it is really not that straightforward. Here are some reasons why:
Hearing aids amplify sounds of different frequencies by different amounts. Most people have lost more high frequencies than low, and therefore need more amplification in the high frequencies. The range of sounds you hear is split into frequency bands or channels, and the hearing aids are set to provide the right amount of hearing at each frequency level.
Less than six channels, and this cannot be done with much accuracy, so six is the magic number. However, a six-channel aid is typically very basic with few other features and is suitable only for hearing a single speaker in a quiet room. The number of channels is not what you should be looking at; it's more the rest of the technology that comes with them.
As a final note, different manufacturers have different approaches. One method is not necessarily better than any other. For example, some manufacturers have as many as 64 channels in their top aids. Most tend to have between 17 and 20. One manufacturer has no channels at all.
Manufacturer's warranties typically last between 2-5 years, depending on the brand and model, and cover defects in materials and workmanship. This includes repairs for component failures, electronic malfunctions, and manufacturing defects, but excludes damage from misuse, accidents, or normal wear. Most manufacturers also include loss and damage insurance for the first year.
We handle all warranty claims on your behalf, liaising with manufacturers and ensuring you get replacement devices quickly when needed. This comprehensive warranty coverage, combined with our lifetime aftercare, gives you complete peace of mind.
Our hearing tests are completely free, whether at our clinics or in your home. Unlike other providers who charge £30-£100 for home visits, we believe hearing healthcare should be accessible without financial barriers. Our comprehensive assessments include examination by a registered audiologist, audiogram results, and personalised recommendations.
All testing, future adjustments, and ongoing support are included at no extra cost. While NHS tests are also free, typical 6-week waiting periods often lead people to seek immediate private testing. We provide prompt, professional assessments that fit your schedule and budget.
Yes, we offer completely free home visits throughout the UK, and this service is included in our prices with no additional charges. Home visits are particularly valuable for people with mobility issues, busy schedules, or those who simply prefer the comfort and convenience of their own environment.
Our audiologists can conduct full hearing tests, fit hearing aids, and provide ongoing support in your home. This service sets us apart from many providers who either don't offer home visits or charge extra for them.
We can offer prices up to 40% lower than high street retailers because of our business model. As a network of 200+ independent audiologists, we don't have the massive overheads of large retail chains - no expensive high street premises, no sales targets pushing audiologists to sell the most expensive options, and no costly marketing campaigns.
However, we maintain the same buying power as the big chains because we purchase on behalf of our entire nationwide network. This means you get access to the same premium hearing aids with professional service, but at genuinely competitive prices.
We offer a comprehensive 60-day money-back guarantee, which gives you twice the industry standard time to properly assess whether your hearing aids are right for you. This extended period recognises that adjusting to hearing aids takes time, and your brain needs several weeks to adapt to the amplified sounds.
Unlike many providers who offer just 30 days, we believe 60 days gives you the confidence to test your hearing aids in all the situations that matter to you - from quiet conversations at home to busy restaurants and outdoor activities.
Ask the Experts
6 Morton Lane
Walkwood
Redditch
Worcestershire
B97 5QA
Latest Launch
When we refer to a product as 'Latest Launch', we mean it is the latest to be released on the market.
New
When we refer to a product as 'New', we mean that the product is the newest hearing aid model on the market.
When we refer to a product as 'Superseded', we mean that there is a newer range available which replaces and improves on this product.
Older Model
When we refer to a product as an 'Older Model', we mean that it is has been superseded by at least two more recent hearing aid ranges.
