Free home visits
with a local audiologist

If you're in search of hearing tests near you, look no further. Our convenient and accessible services provide quick and accurate assessments of your hearing health. Located in your local area, our certified professionals offer comprehensive hearing tests that cater to individuals of all ages.
We employ state-of-the-art equipment to ensure precision and reliability. Early detection of hearing issues is vital, and our testing facilities are committed to identifying problems promptly. Your improved communication, safety, and overall well-being are just a visit away.
However, on this page, we talk about everything you need to know about hearing tests, hearing aid fittings, and programming in the clinic as well as the importance of regular testing.

We often wonder why people put off getting their hearing tested. Early diagnosis is paramount to receiving the best treatment and determines the success of your hearing healthcare. Maybe it is due to not understanding the dangers of long-term untreated hearing loss.
Putting off seeking professional help and living without amplification, your perception of sound can change. This is never a good thing. Perhaps it’s because they feel there is a stigma surrounding hearing loss and see it only through negative eyes.
No one wants to be seen as old and some people see hearing loss as a sign of this. What they don’t understand is how discrete and modern the hearing solutions are today. Early diagnosis is vital to ensure hearing aids are correctly programmed to your own unique hearing loss – if hearing aids are what’s needed.
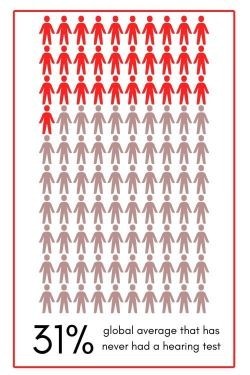
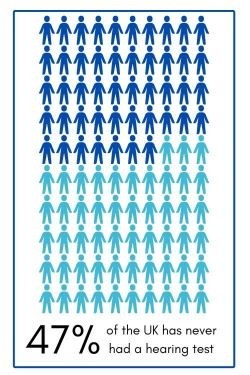
Or it might be that they are anxious and don’t know the true process of a hearing test and audiogram. What does it look like? How is it created? How is it used? Or they might be unsure how to interpret audiogram results and how to understand audiogram hearing loss levels.
A good audiologist will everything clear and ensure you understand the steps needed for a hearing test. This way you will have a better understanding and will, in turn, feel more confident. Here we answer those questions for you, in the hope, it will help you to make the right decision in getting help.
What is an audiogram? To put it simply, an audiogram is a hearing test graph that shows the results of your test with an audiologist. It displays one part of your complete assessment and is the most useful tool to piece together your hearing capabilities. Your audiologist will explain, simply, what the results show concerning your volume, pitch, and speech sounds.
Your audiologist will be reading an audiogram to gain a clearer insight as to the level of any hearing loss and potentially the most probable cause. If any other medical issue is apparent, then your audiologist will refer you to an ENT specialist.

How does an audiogram work? What happens at a hearing test? Well, while you are being tested sounds are sent to you at various pitches and volumes using a computer-driven audiometer. This allows an audiologist to adjust the pitch of those sounds manually and at what intensity.
You will respond to these sounds by pressing a button to indicate when you hear them. The quietest level of each sound you hear is recorded at each pitch – then plotted on the audiogram. An audiologist will use a red circle for your right ear and a blue one for your left.
These recordings, using the circles, are comparisons to normal hearing levels of 25dB overall pitches of sound. The further down the results are on the graph, the louder the sound has had to be adjusted.
A good audiologist will take their time and allow for around an hour to fully assess your hearing ability, however, the actual hearing test will take about 20-30 minutes to complete. After that, your audiologist will go through your diagnosis thoroughly using your audiogram results and list the options available to you.
They will help you decide, if needed, the best hearing solution for you and your hearing loss needs along with making plans for your hearing aid fitting, follow-up appointment, and treatment going forward. Depending on availability and the hearing aid model, they might be able to fit and program your hearing aid then and there.
Hearing tests, also known as audiometric evaluations or audiograms, are a crucial aspect of hearing healthcare in clinics. These tests are used to determine the nature and level of an individual's hearing loss, if any, and to guide the selection and fitting of hearing aids or other assistive devices that would support their hearing healthcare going forward.
The results will also be used to monitor the progression of hearing loss over time and to evaluate the effectiveness of any treatment that is provided.
It all depends on how exposed you are to harmful sounds. For example, if you work on a building site - you would need to have an annual hearing test. However, you should get your hearing checked immediately if you think your hearing might have changed - even if you already wear hearing aids.
Other than that, on average, we would recommend testing your hearing at least every three years - unless your audiologist has stated otherwise. Consistent hearing healthcare is vital in order to prevent further deterioration and improve the individual's quality of life.

Both the air and bone conduction results of the pattern and position for both ears are read by the audiologist. They determine the level, nature, and cause of the results shown and highlight problematic ranges. Some people may refer to an audiogram as a 'hearing test chart' or 'hearing test graph'.
The audiogram’s vertical axis shows the volume or intensity of the sound given – measured in decibels (dBHL). It begins at 10 dBHL and finishes at 120 dBHL. The horizontal axis displays where the low-pitch sound starts and escalates in pitch as you go through your test.
When the audiologist reads the results for both ears and finds a level of hearing loss, it generally is found in both ears. However, sometimes there can be asymmetry and varying levels. Your air and bone conduction tests are compared, and you will be shown if this is the case and if your loss is sensory-neural, conductive, or both.
What are decibels & what are frequencies? Decibels are what we measure sound and are not permanent values like volts and meters. This scale is logarithmic and doubles the sound pressure level, increasing by 6dB. The dB scales vary according to the environment the sound travels through, using a calibrated decibel hearing level scale.
Frequency is the number of vibrations per second in each sound wave and is measured in Hertz (Hz). The higher the level, the higher the frequency. The vibrations used are between 20 and 20,000 Hz and reflect the sounds heard by us every day. Nature sounds, such as bird songs, would be a high tone and a bass guitar would be a low one.
If you have a high-frequency loss it generally means that you have problems hearing high-frequency sounds only. Consonants like s, f, sh are hard to make sense of. Whereas low-frequency loss – being less common – affects the ability to hear vowels in conversation.

As a routine, hearing tests for newborn babies are carried out in the hospital to quickly identify any problems at the start of their development. This is called a newborn hearing screening. Following this, children's parents are generally asked from 9 months to 2 and a half years of age if they have any concerns regarding their child's hearing.
Then a hearing test is done around the time children start school - either in school or at the hospital.
Hearing problems in childhood are not common, but hearing tests for kids of all ages can be done through the NHS or private. It is important to always check children's hearing if there are any concerns, as early testing makes sure that any issues are diagnosed and managed as early as possible.
Wondering how much does a hearing test near me cost? Wherever you go for your hearing test it should be free, but some hearing aid providers do charge - especially if you want to test your hearing at home. We recommend you ask your audiologist before you book your appointment to avoid any disappointment.
At Hearing Aid UK, all our hearing tests, aftercare, digital hearing aid fitting, and programming are included in the price of the hearing aid(s).
The NHS provides free hearing tests and usually, your GP will refer you to the NHS to book an initial appointment with an audiologist. Because it normally takes up to six weeks to get an appointment, patients often get tested privately instead.
Hearing is a fundamental aspect of human communication, and any impairment can have a significant impact on an individual's quality of life. Here are several reasons why regular hearing tests are important:
Early detection of hearing loss: Regular hearing tests can help identify hearing loss at its earliest stages. This is crucial because many forms of hearing loss develop gradually and individuals may not even realise they have a problem until it has progressed significantly.
Early detection allows for prompt intervention and treatment.
Improved communication: Hearing is a fundamental aspect of communication. Those with hearing loss often struggle to understand conversations, which can lead to frustration, social isolation, and strained relationships.
Regular hearing tests can detect and address issues early, enabling individuals to maintain effective communication with friends, family, and colleagues.
Quality of life: Untreated hearing loss can significantly reduce a person's quality of life. It can lead to depression, anxiety, and a decreased ability to participate in social activities.
By identifying and addressing hearing problems, individuals can enjoy a higher quality of life, remain socially engaged, and experience less emotional distress.
Safety: Hearing loss can jeopardise one's safety. It can make it difficult to hear important auditory cues like sirens, alarms, and horns, potentially leading to accidents or dangerous situations.
Regular hearing tests can help ensure that individuals remain safe in their daily lives.
Cognitive health: There is a strong connection between hearing health and cognitive function. Untreated hearing loss has been linked to an increased risk of cognitive decline, including conditions like dementia.
Regular hearing tests can help identify issues early, allowing for interventions that may help preserve cognitive function.
Professional success: Hearing impairment can hurt an individual's professional life. It may lead to misunderstandings at work, decreased job performance, and missed career opportunities.
Regular hearing tests can help individuals maintain their professional success and communication skills.
Customised solutions: Regular hearing tests enable audiologists to tailor solutions to each individual's specific needs. Whether it's hearing aids, cochlear implants, or other assistive devices, a proper diagnosis through regular testing ensures that the chosen solution is most effective for the individual.
Prevention of further damage: Some forms of hearing loss, like noise-induced hearing loss, are preventable. Regular hearing tests can help individuals understand the risks they face in their environments and make informed decisions about protecting their hearing.
This knowledge can prevent further damage and preserve their hearing for the long term.
Emotional well-being: Hearing loss can lead to feelings of frustration, embarrassment, and isolation. Regular hearing tests and the subsequent management of hearing issues can help individuals maintain their emotional well-being, confidence, and self-esteem.
Choosing between hearing care in a clinic or at home will depend on an individual's specific needs and preferences. Both options have their own advantages and disadvantages. It may be helpful to talk to an audiologist or hearing healthcare professional to determine the best option for you.
A hearing aid fitting in a clinic is a process that is done to ensure that a hearing aid is properly adjusted and customised to meet the specific needs of an individual with hearing loss. We go through the typical process below:

A consultation is done with an audiologist or hearing aid specialist to discuss the results of the hearing test, as well as the patient's needs and preferences. They will discuss the different types of hearing aids available and which one will be the best fit for the patient.
The patient will select a hearing aid that suits their needs, preferences, and budget.
The hearing aid will be adjusted to the patient's specific hearing loss, and programmed to suit their individual needs. This may involve adjusting the volume and frequency response, as well as fine-tuning the settings to match the patient's unique hearing profile.

The patient will have follow-up appointments to ensure that the hearing aid is working properly and that the patient is satisfied with the fit and performance. The audiologist will also give instructions on how to take care of the hearing aid and how to use it properly.
In conclusion, a hearing aid fitting in a clinic is a process that is done to ensure that a hearing aid is properly adjusted and customised to meet the specific needs of an individual with hearing loss.
The fitting process may take several appointments to ensure that the hearing aid is properly adjusted and customised to meet the specific needs of the individual.
Wondering how to get a hearing test locally? If you are wondering where to get a hearing test near me - it's easy - hearing tests are very accessible and are available on your high street. You can also book a hearing test for free with us.
We offer free hearing tests in the comfort of your own home and free home visits for other hearing healthcare services. We also provide free hearing tests at home for the elderly. For any advice about hearing healthcare or to book a hearing test with an audiologist near you, please contact one of our experts free on 0800 567 7621
Do not spend hundreds of pounds without getting a second opinion from us.
 Not only are the prices great, but the service is fantastic! Many thanks to your team.
Not only are the prices great, but the service is fantastic! Many thanks to your team.Well, while you are being tested sounds are sent to you at various pitches and volumes using a computer-driven audiometer. You will respond to these sounds by pressing a button to indicate when you hear them. An audiologist will use a red circle for your right ear and a blue one for your left. These markings will give your audiologist a bigger picture of how well you hear.
Well, while you are being tested sounds are sent to you at various pitches and volumes using a computer-driven audiometer. You will respond to these sounds by pressing a button to indicate when you hear them. An audiologist will use a red circle for your right ear and a blue one for your left. These markings will give your audiologist a bigger picture of how well you hear.
A good audiologist will take their time, however, a hearing test will generally take about 20-30 minutes to complete.
When we refer to a product as 'Latest Launch', we mean it is the latest to be released on the market.
When we refer to a product as 'New', we mean that the product is the newest hearing aid model on the market.
When we refer to a product as 'Superseded', we mean that there is a newer range available which replaces and improves on this product.
When we refer to a product as an 'Older Model', we mean that it is has been superseded by at least two more recent hearing aid ranges.